Inflammation increases the risk of heart disease and cancer. But does inflammation cause weight gain too? Turns out inflammation can influence weight, thanks to the way it disrupts insulin sensitivity, metabolic speed, gut health, and more. But there are ways to lower inflammation and drop some pounds at the same time.
Inflammation is a hot topic for a reason. For one, high levels of chronic inflammation may cause chronic fatigue syndrome, heart disease, and even cancer. Also, with both inflammation and obesity on the rise in the U.S.—over three-quarters of Americans now qualify as obese or overweight—many of us are wondering: Does inflammation cause weight gain?
There’s a lot to unpack about the relationship between inflammation and weight gain—and how to reduce both for your overall health.
What is chronic inflammation?
What is inflammation, in the first place? Think about a time you got a nasty cut. Most likely, it swelled up or turned red while it was healing. That reaction is a sign of inflammation.
Inflammation is the immune system’s response to a germ, foreign objects, or an injury. It’s marked by five main symptoms:
- Redness
- Heat
- Swelling
- Pain
- Loss of function (i.e. having a poor ability to smell when you're sick, or the inability to move an inflamed knee)
Not all five symptoms are present in every case of inflammation—and to make matters even more confusing, some inflammation occurs without any symptoms.
More often than not, inflammation is acute, meaning it’s a short-term response to an injury or infection—and when acute, it’s actually useful for getting rid of injuries and infections and to promote healing. Where problems arise is when inflammation persists and doesn’t resolve.
“Unlike acute inflammation, chronic inflammation occurs when the body’s immune system remains active for an extended period, even when there is no immediate threat,” says Steven Shamah, M.D., the director of endoscopy at Lenox Hill Hospital. He adds that chronic inflammation can damage tissues and organs and even contribute to various chronic conditions, such as heart disease, arthritis, and autoimmune conditions.
Common causes of chronic inflammation
Acute inflammation’s cause are often cut and dry: An injury, illness, or other disturbance to the body. Chronic inflammation, though? Well, that’s a bit more complicated.

Chronic inflammation typically stems from everyday life and our habits, though the risk of chronic inflammation also increases as we age. It can also be caused by an indolent infection like Lyme, or mold and toxins like heavy metals (i.e. mercury from fish). The most common habits linked to chronic inflammation include:
- Diet: An ultra-processed diet or one that’s high in sugars increases the risk of chronic inflammation.
- Weight: Being overweight or obese puts someone at a higher risk.
- Stress: Feeling worried or stressed constantly is a risk factor for chronic inflammation.
- Sleep: A lack of quality sleep may contribute to chronic inflammation.
- Smoking: Cigarette smoking may elevate the risk of chronic inflammation.
- Hormonal imbalance: When imbalanced, certain hormones (specifically estrogen or testosterone) increase the risk of chronic inflammation.
Not sure what your symptoms are really telling you?
The Parsley Symptom Index helps connect the dots across your whole body so you can understand patterns, not just isolated symptoms.
The links between inflammation and weight gain
The question “does inflammation cause weight gain?” has a one word answer: yes. And weight gain can cause inflammation too. A more nuanced question is how inflammation causes weight gain. And the latter has a more complicated answer.
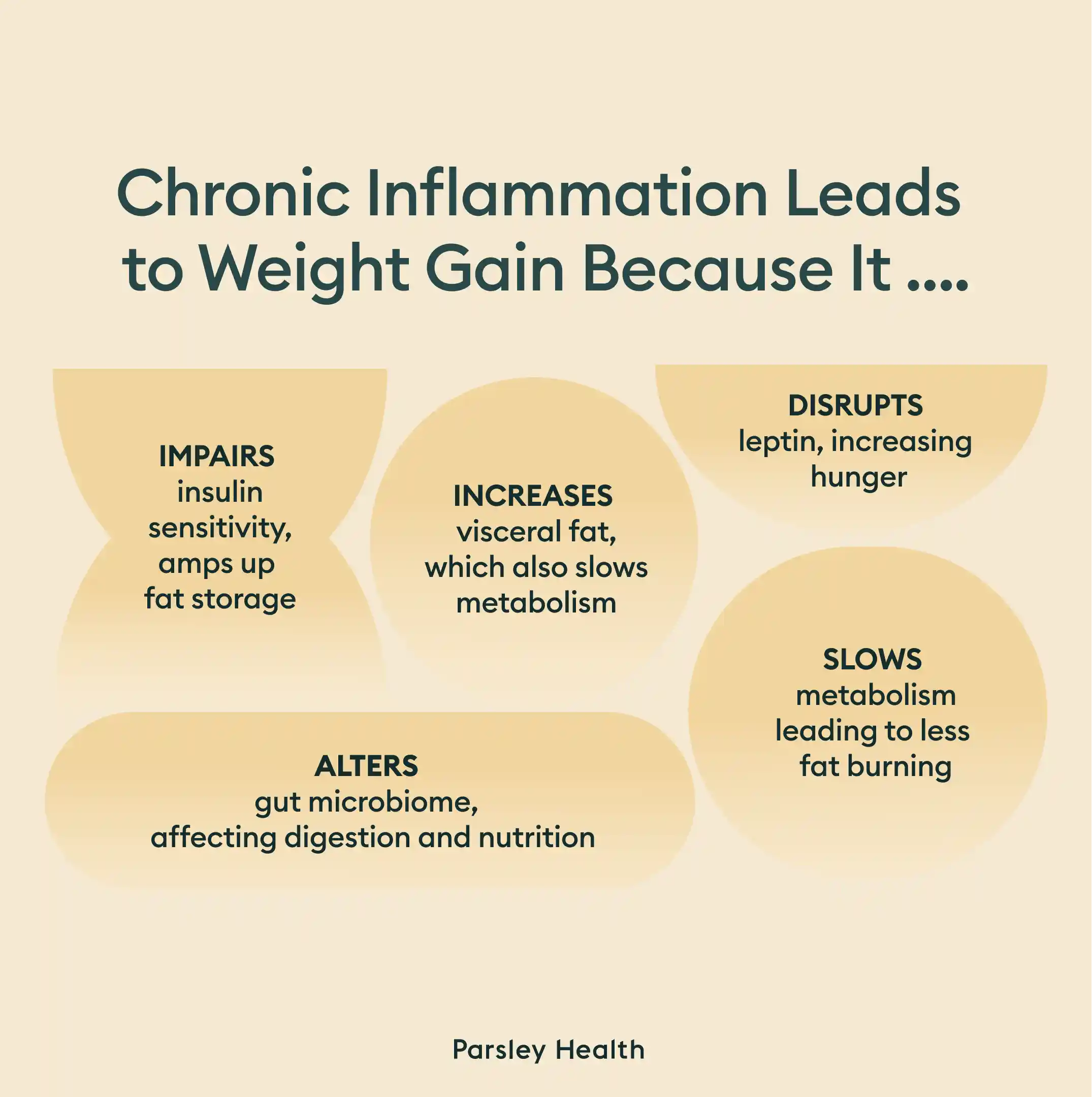
Long story short: Inflammation causes weight gain by disrupting hormones, impacting metabolism, disrupting the gut microbiome, and promoting visceral fat accumulation. If that sentence overwhelms you, don’t worry. We’re about to dive into what each cause means.
How inflammation impacts metabolism
When I say the word metabolism, what comes to mind? If you’re anything like me, weight probably came up pretty quickly. Inflammation may not have been something you considered. Yet, it plays a crucial role in determining our metabolic rate.
Cytokines, a type of inflammatory marker, helps the body control its metabolic rate. When there is too much inflammation in the body, cytokines slow down the metabolic rate—and a slower rate means less burned fat, increasing the number on the scale.
Hormonal disruptions caused by inflammation
Hormones provide important cues for our body, including messaging around when to burn off proteins, carbs, and fat and when to store them. Chronic inflammation, however, disrupts two key hormones, insulin and leptin.
“Inflammatory messengers (e.g., cytokines) impair insulin sensitivity,” says Jason Itri, M.D., a radiologist based in Florida. While we commonly think of insulin as a diabetes medication, it’s also a naturally occurring hormone in the body that helps store excess calories as fat. When inflammation disrupts insulin sensitivity, the body stores more fat and reduces calorie-burning efficiency—and fewer calories burned often means weight gain.
While insulin controls fat storage, leptin is responsible for hunger cues. Under normal circumstances, it helps us feel full and stops hunger. Chronic Inflammation causes leptin resistance and leads to lower satiety triggering an increased appetite.
Gut health and weight gain
“Inflammation of the gut alters the gut microbiota and disrupts the gut barrier,” says Dr. Itri. Both of these can have a long-lasting impact on how much someone weighs. The gut microbiome is a collection of bacteria and fungi that impact digestion, as well as other bodily functions (think: mental health, skin health, immune system, and so on).
While powerful, it’s susceptible to external influences. What we eat, the medications we take, and how much we exercise all influence whether there are more good or bad bacteria in the gut. Chronic inflammation can alter the gut microbiota, usually tilting the scales toward more of the bad than good. Bad gut bacteria negatively impacts digestion, which may lead to someone gaining weight.
The second way inflammation influences gut health is by disrupting the gut barrier. The intestinal lining (aka gut barrier) controls what enters and leaves the gut. When it’s disrupted, bad particles can leave and enter. While scientists are still exploring all the impacts of increased intestinal permeability, one is probably weight gain.
Inflammation and burning fat
“Inflammation can affect how the body burns fat and uses energy, often leading to an increased risk of weight gain or difficulty maintaining a healthy weight,” says Dr. Shamah, adding that chronic inflammation can increase the amount of visceral fat.
Visceral fat, also referred to as belly fat, slows metabolic activities. Those who are obese or overweight often possess higher levels of visceral fat, indicating this fat may play a role in weight gain.
To make matters more confusing, visceral fat also increases inflammation in the body. Basically, chronic inflammation increases the rate of visceral fat and visceral fat increases inflammation, creating a vicious cycle that puts someone at risk of higher inflammation levels and weight gain.
The psychological impact of chronic inflammation on weight gain
Chronic inflammation doesn’t only influence hormones, metabolism, fat storage, and the gut. It also plays a role in our mood. Many mental health conditions have a direct link to chronic inflammation, meaning the more inflammation, the higher the chance of feeling fatigued, depressed, or anxious.
I don’t know about you, but whenever my mood is low or I feel fatigued, the last thing I want to do is exercise or eat healthy. Breaking the feedback loop between chronic inflammation and our mental health is key to developing healthy habits.
Can reducing inflammation help with weight loss?
Reducing inflammation can do a few key things to help with weight loss:
- Preserve a normal metabolic rate
- Restore hormones like insulin and leptin to their normal rhythm
- Stop increased intestinal permeability and gut microbiome alterations
- Prevent unnecessary fat storage
- Possibly revive psychological motivation to eat healthy and workout
But even if the links are clear, it’s easier to just focus on weight loss, right? While it might seem like concentrating solely on losing weight is the way to go, it doesn’t address the root cause. When we address the symptom (weight gain) without looking at the underlying reason (inflammation), we’re fighting an uphill battle that will leave us exhausted and without the results we want.
Healing stories from our members
Effective strategies to reduce inflammation
Ok, so we’ve established that we need to address the root cause—but finding ways to do so is another matter. To help, here are some dietary and lifestyle changes that can lower inflammation.
Anti-inflammatory diet
We can’t control everything that increases inflammation, but we can control our diet. Adding anti-inflammatory foods to our plate often works best. If curious about specific anti-inflammatory foods, here are some to consider:
- More vegetables and fruit
- Whole grains
- Foods with omega-3 fatty acids, like salmon and flaxseed
- Herbs and spices
At the same time, it’s best to avoid (or enjoy in moderation) inflammatory foods, such as ultra-processed foods, sugars, refined carbs, and alcohol.
Gut health and inflammation
Remember when we discussed how poor gut health and chronic inflammation played off each other? Well, one way to address both is to balance the gut microbiome. Specifically, you want to consume more probiotics (in sauerkraut, yogurt, and miso, among other foods) and prebiotics (in foods such as asparagus, oats, and bananas). Both help balance the gut microbiome when consumed as whole foods or a supplement.
Another key to good gut health is to eat a high-fiber diet. While the body turns most carbs into usable energy quickly, it cannot do so with fiber because it’s harder to break down. Instead, fiber moves through our intestines without being absorbed, meaning we feel full longer. As an added bonus, fiber cleans out the colon, keeping our digestive tract in tip-top shape.
For grocery store inspiration, here’s a non-exhaustive list of fiber sources:
- Sunflower seeds
- Brown rice
- Green beans
- Chia seeds
- Beans
- Carrots
- Pumpkins
- Broccoli
- Apples
- Red bell peppers
Lifestyle adjustments
So far, many of our strategies to reduce inflammation focus on diet. While what you eat plays a crucial role in lowering chronic inflammation, it isn’t the only factor. You also want to focus on sleep, stress, and movement.
When it comes to sleep, aim to get seven to nine hours of quality sleep each night. This will help reset the circadian rhythm, balance hormones, and can even reduce stress. Other stress management techniques include breathwork, meditation, and practicing mindfulness.
The third habit that can reduce inflammation is regular movement—and note that we used movement, not exercise. While a rigorous workout may help lower inflammation levels, mild to moderate aerobic movement (i.e. a bike ride or walk) will do the trick too—and may be easier to stick with.
When to seek medical advice
“Persistent or worsening symptoms lasting several weeks without an acute event merit a visit to a healthcare provider,” says Dr. Itri. He adds the symptoms to look out for include unexplained weight gain, chronic pain, swelling, digestive issues, frequent infections, or prolonged recovery from injuries.
Ideally, you want to make an appointment with a functional medicine provider who will look at the root cause of your symptoms. Functional providers can also order tests to measure CRP levels and/or cytokine levels, both of which indicate inflammation levels in the body.
When inflammation is high, a functional provider will help you create an anti-inflammatory plan customized to your lifestyle and needs. If inflammation isn’t to blame, they can run other diagnostic tests to determine the root cause of any weight gain.
Parsley Health offers physician-led functional medicine care, advanced lab programs, and flexible ways to get started, all designed to help you feel better over time.
Key takeaways
So, can inflammation make you gain weight? The answer is a resounding yes. Chronic inflammation leads to weight gain in a few key ways:
- Slows metabolism: Chronic inflammation slows the metabolic rate and signals to the body to store more fat. In turn, this leads to increased weight, especially around the belly.
- Disrupts hormones: Chronic inflammation can disrupt many hormones, including insulin and leptin. Insulin helps the body decide when to store and burn calories. If disrupted, the body may not burn enough calories. Leptin helps cue the body when it’s time to eat. When disrupted, the body feels hungry more often.
- Imbalances the gut: Last but not least, chronic inflammation disrupts the gut microbiota and increases intestinal permeability, two factors associated with higher rates of obesity and being overweight.
If concerned that inflammation may be to blame for any weight changes, reach out to Parsley Health. Our doctors regularly consult on weight and inflammation, run tests to identify your inflammation level, and create a customized plan to lower inflammation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Do you weigh more if you have inflammation?
While inflammation in and of itself doesn’t make you weigh more, it disrupts hormones and fat storage, metabolism rate, insulin sensitivity, and gut health. As a result, high levels of chronic inflammation can cause weight gain.
How to get rid of inflammation weight?
To get rid of inflammation weight, focus on the root cause: Chronic inflammation. Implementing an anti-inflammatory diet, balancing the gut microbiome, regular movement, getting seven to nine hours of sleep per night, and reducing any stress all reduce inflammation levels.
Does inflammation make it harder to lose weight?
When chronic, inflammation makes it harder to lose weight. Chronic inflammation slows someone’s metabolic weight, disrupts gut health, and impacts how much fat the body stores. These factors, in turn, mean your body is working to store more weight than it needs.
What is the fastest way to reduce inflammation in the body?
Some of the fastest ways to reduce inflammation in the body include switching to an anti-inflammatory diet, reducing stress, and balancing the gut microbiome through eating more prebiotics, fiber, and probiotics. Avoiding inflammatory foods (think ultra-processed or high in sugar) and alcohol can also help.









